Model
Anitferromagnetic Ising model Hamiltonian
density operator
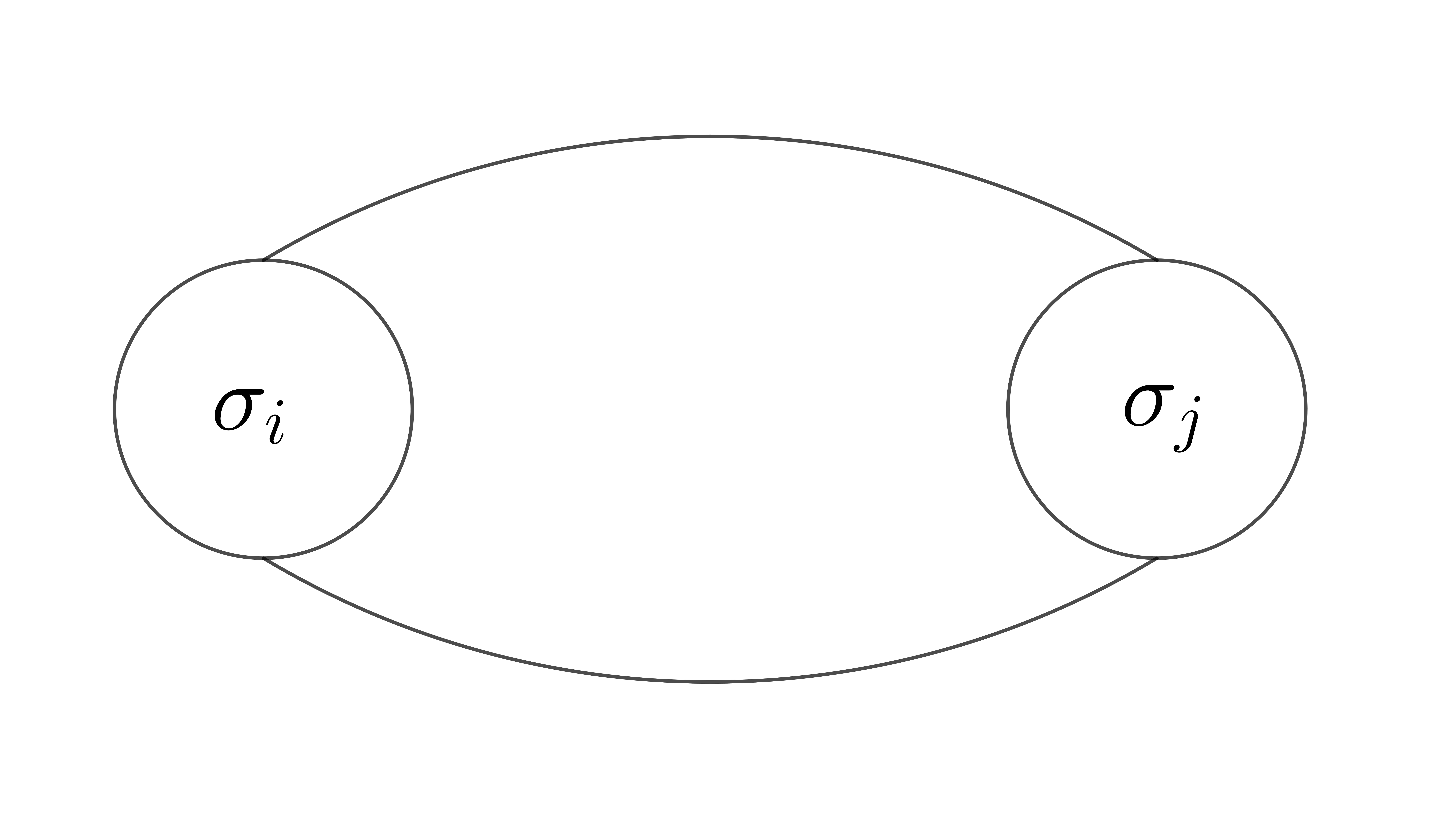
3 lattice

4 lattice

变换
求法
若
则
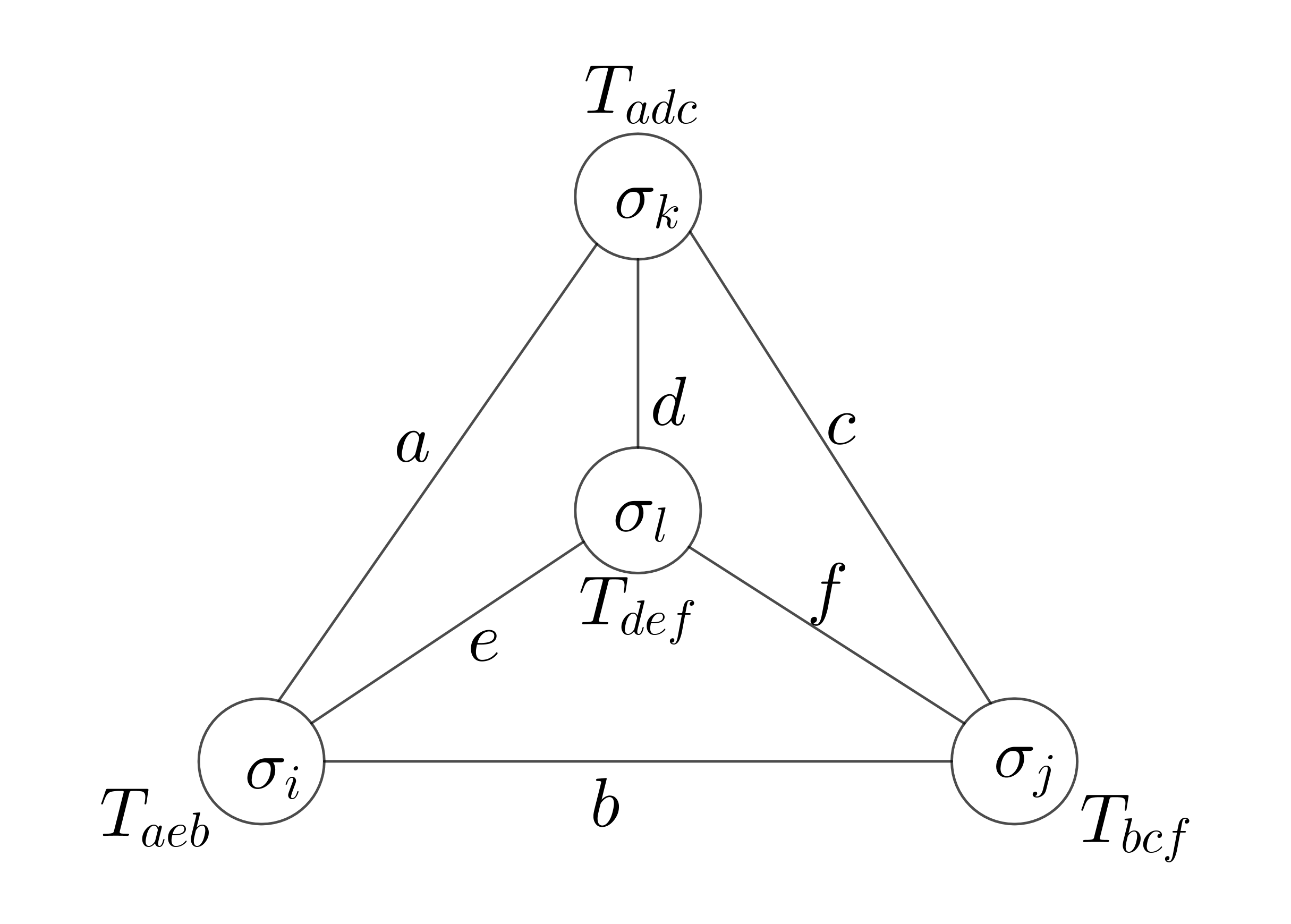
Tensor
partition functiom
 |
 |
 |
xxxxxxxxxx"""This is a triangle lattice of Ising model.Using tensor network method to get the partition, ground state energyand degeneracy of ground state energy.In addition, also calculate the exact partition function."""import numpy as npimport torchfrom scipy import gradientfrom scipy.linalg import sqrtmfrom torch.autograd import Variablefrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt# define a function: compute the value of derivetive of function f(x)# at x = a. Number of setps is N, and compute in the region [a-l, a+l]def mydiff(f,a, N = 1e3, l = 1e-2): s = 2*l/N x = np.linspace(a-l,a+l,N) fun = np.linspace(0,0,N) for i in range(int(N)): fun[i] = f(x[i]) d = gradient(fun,s) d = d[int(N)//2] return dbeta = 100# compute the partition function Zdef getZ(beta,mu=0): B = np.array([ [np.exp(-beta), np.exp(beta)], [np.exp(beta), np.exp(-beta)] ]) B = B*np.exp(beta*mu) A1 = torch.tensor(B) Z = torch.einsum('ij,jk,ki->',A1,A1,A1) Z = Z.numpy() return Zprint('Z=',getZ(beta))# compute lnZdef lnZ(beta): Z = getZ(beta) Z = np.log(Z) return Z# when 1 is negleticable compare to beta, E is the ground state energy.E0 = -mydiff(lnZ, beta, N = 1e2, l = 1e-4)#E0 = np.around(E0)print('E0 = ',E0)#print('zzdaf', lnZ(.999))mu = -1/3# whe mu is equal to groud state energy E0/number of interactiondef Deg(beta,mu=mu): Deg = getZ(beta,mu=mu) return Degprint('degeneracy is',Deg(beta))ZZ = (2*np.exp(-3*beta) + 6*np.exp(beta) )#*np.exp(-100)print('exact partition function is', ZZ)xxxxxxxxxxZ= 1.6128702850896815e+44E0 = -1.0101010126106758degeneracy is 6.000000000000087exact partition function is 1.6128702850896815e+44
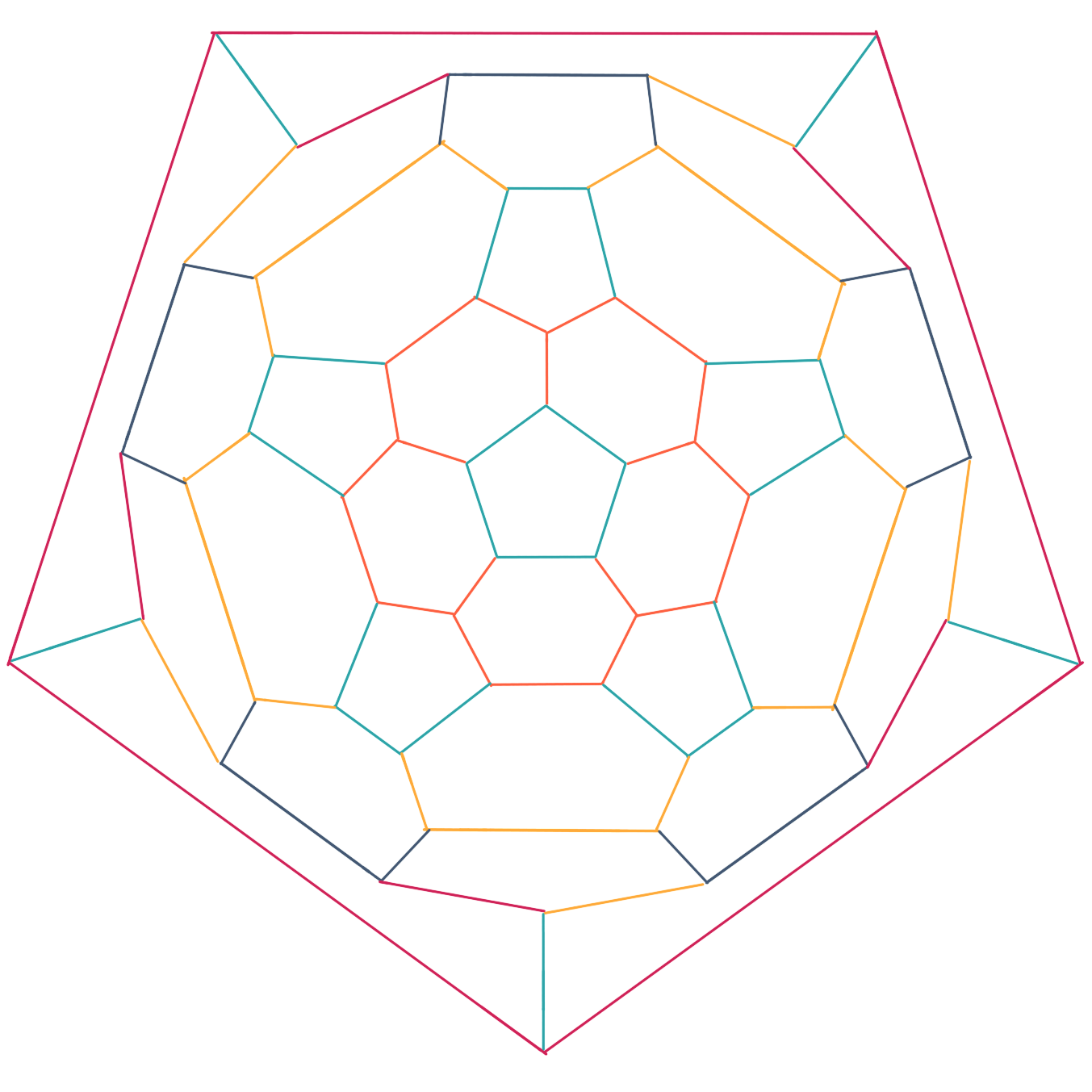 |
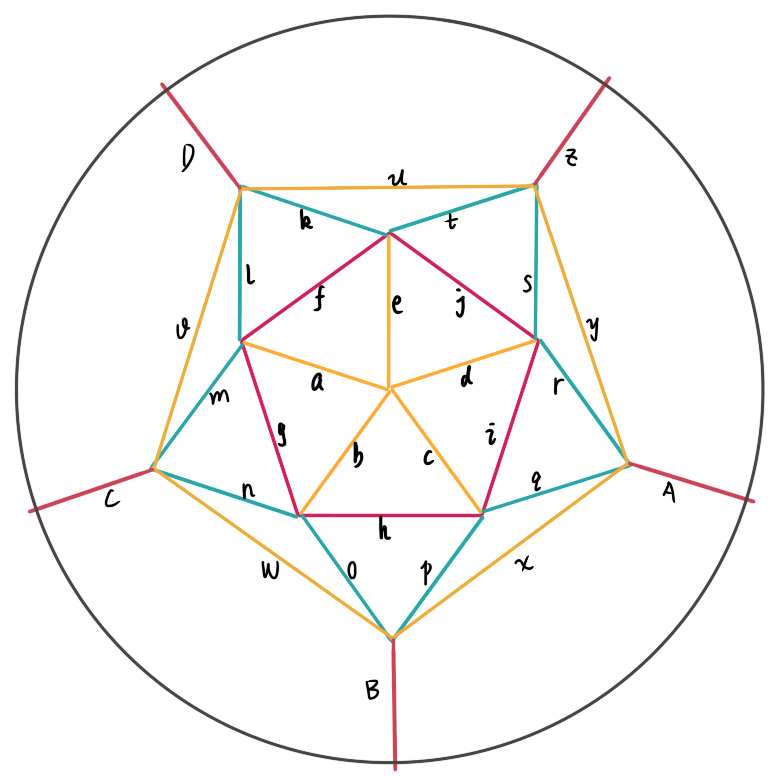 |
xxxxxxxxxx"""This is a python3.7 code to calculate the ground state energy of aIsing model of C60 using tensor network methodcopyright: Copyright 2019 by ZQW.license: MIT"""import numpy as npfrom scipy.linalg import sqrtmdef mydiff(f,a,b,N): """ get the derivative of function f: the input function N: calculate the derivatives of function f at N points in [a, b] return: N derivatives of function f """ fx = np.zeros(N) s = (b-a)/(N-1) d = np.zeros(N-1) for i in range(N): x = a+i*s fx[i] = f(x) print('f(',x,')=',fx[i]) if i>0: d[i-1] = ( fx[i] - fx[i-1] ) /s print('f\' between',x,'and',x-s,'is',d[i-1]) return ddef getlnZ(beta): S = np.array([ [np.exp(-beta), np.exp(beta)],\ [np.exp(beta), np.exp(-beta)]]) # the S matrix # between two lattice S = sqrtm(S) T = np.einsum('ij,ik,il->jkl',S,S,S) # the 3-tensor at each lattice T = np.einsum('iae,jab,kbc,lcd,mde->ijklm',T,T,T,T,T) # the # 5-tensor at each lattice of a icosahedron after contraction of 12 pentagon Z = np.einsum('abcde,kfejt,jdirs,ciqph,hongb,mgafl,\ ABCDz,Ayrqx,Bxpow,Cwnmv,Dvlku,zutsy->'\ ,T,T,T,T,T,T,T,T,T,T,T,T) # contract the 12 # lattices of the icosahedron to get the partition function of C60 Z = Z.real lnZ = np.log(Z) # the log of partition of C60 return lnZE0 = - mydiff( getlnZ, 1,12,12) # according to statistical mechanics# to get the energy. when temperature is 0, it is the ground state energy.print(E0)xxxxxxxxxxf( 1.0 )= 78.4421074656477f( 2.0 )= 142.01437800946442f' between 2.0 and 1.0 is 63.57227054381673f( 3.0 )= 207.72503688198492f' between 3.0 and 2.0 is 65.7106588725205f( 4.0 )= 273.6863836975408f' between 4.0 and 3.0 is 65.96134681555588f( 5.0 )= 339.6811612250026f' between 5.0 and 4.0 is 65.99477752746179f( 6.0 )= 405.6804545976738f' between 6.0 and 5.0 is 65.99929337267122f( 7.0 )= 471.680358971803f' between 7.0 and 6.0 is 65.99990437412919